No time to read? Just listen to the news!
TL;DR
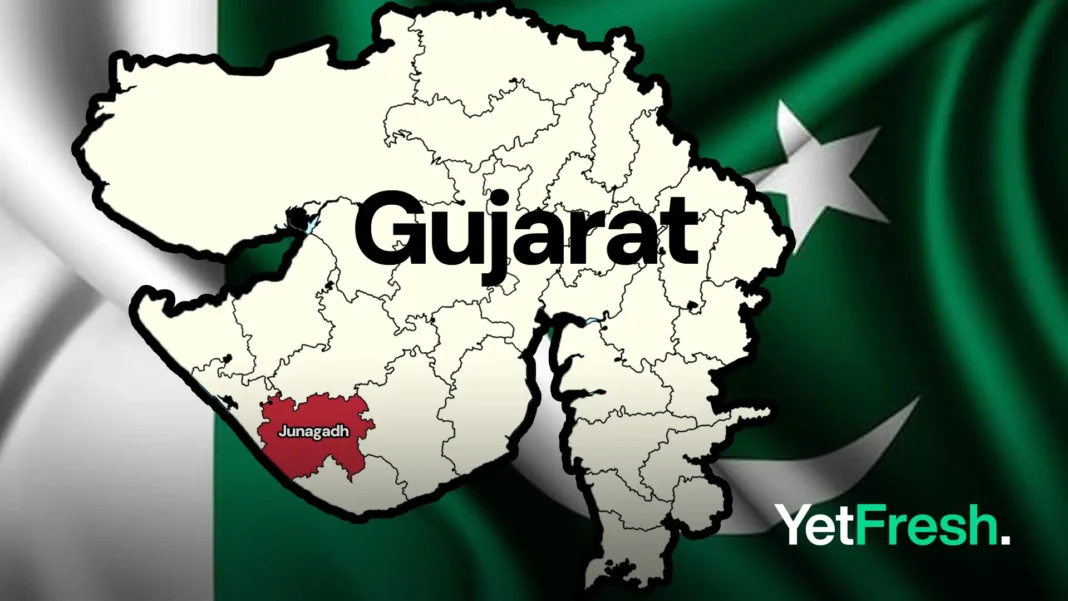
- Pakistan claims Junagadh, a city in India’s Gujarat state, as its own, asserting that India has illegally occupied the region since 1948.
- Mumtaz Zahra Baloch, Pakistan’s Foreign Affairs Ministry spokesperson, states that Junagadh’s accession to Pakistan during the 1947 partition is historically and legally justified.
- Pakistan has consistently raised the Junagadh issue on political and diplomatic platforms, considering it an unresolved matter similar to the disputed Jammu and Kashmir region.
- India rejects Pakistan’s claims, deeming the inclusion of Junagadh in Pakistan’s official map as unreasonable, baseless, and a reflection of Pakistan’s territorial ambitions.
On Tuesday, Pakistan reignited a long-standing territorial dispute with India by claiming sovereignty over Junagadh, a city located in the western Indian state of Gujarat. During a press conference, Mumtaz Zahra Baloch, spokesperson for Pakistan’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs, asserted that Junagadh had acceded to Pakistan at the time of the partition in 1947, but was subsequently “illegally occupied” by India.
Baloch emphasized that the people of Pakistan view the issue from both historical and legal perspectives, maintaining that Junagadh is an integral part of Pakistan. She accused India of violating the UN Charter and international law through its alleged illegal occupation of the region.
The spokesperson further claimed that Pakistan has consistently raised the issue of Junagadh on political and diplomatic platforms, considering it an unresolved matter akin to the disputed territory of Jammu and Kashmir, which Pakistan refers to as “India’s illegally occupied Jammu and Kashmir.”
The renewed focus on Junagadh has led some to speculate whether Pakistan is attempting to divert international attention from the Kashmir issue to India’s western frontier. The dispute between the two neighboring countries over Junagadh dates back to their independence in 1947, with the controversy resurfacing in 2020 when Pakistan included several Indian regions, including parts of Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, Junagadh, Manavgarh, and the Sir Creek region, in its official map.
India has consistently rejected Pakistan’s claims, deeming the political map “unreasonable and baseless” and characterizing the inclusion of Junagadh as a reflection of Pakistan’s “ambitions” rather than a legitimate territorial claim.
The recent statements by Pakistan’s Foreign Affairs Ministry spokesperson have once again brought the long-standing dispute to the forefront, underscoring the complex historical and political tensions that continue to shape the relationship between the two South Asian nations.
Source: Ekattor TV